
aaptekgsm
A K M P T A
|
Attention : amct team is a subsiediary of A.K.M.P.T.A
|
|
| | Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks |  |
|
+8kerryzeng kladeed master_mudieee nighthawk BONUO CELL ™ AMCT KNR AAPTEK FULLFLASHGSM 12 posters | |
| Author | Message |
|---|
FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Fri Sep 24, 2010 11:36 am Fri Sep 24, 2010 11:36 am | |
| First topic message reminder :
How to repair dead phone
Problems or trouble typically found on mobile phones can be categorized into
Three damage categories, namely:
1. Software Problem category
2. Hardware Problem category
3. Problem Category his SW and HW
Phone problems and solutions
1. Total dead cell phone
Mobile phones exist three kinds of die total, die total because of
· Die alone,
· Total death due to falls, and
· Death total for the taxable water.
a. Total death because death itself.
Handling:
The first can be done early steps following
- Remove the battery and plug in again, or try using another battery and try turn it
- Check the battery connector and try the press to see the level of flexible or not,
replace damaged when new.
- Connect the charging of the phone, when the indicator on the phone in and still will not turn on, then obviously you can not live on mobile phones because of interference from IC PA (Power Amplifier). After IC PA revoked your mobile phone can turn it on again. And so no signal will be installed a new PA IC.
- When the tide does not exist and charging indicator on the phone still does not want to live on should be conducted further tests using power supply. But there may also have an ugly tin on the PCB, remove the IC PA solution, then clean the tin on the PCB where IC PA stick, replace the old IC PA, HP switch, it must be a flame.
Examination with power supply:
Necessary power supply on a scale of 1 ampere ampere (A) or 1000 mA.
With the aim that the examination can be more easily and clearly.
The steps are as follows:
- Connect the cable from the power supply to the mobile phone battery connector of at least three wires, with a negative sequence, BSI and positive. (Black, green and red)
- Navigate volt power supply at 3.6 V (or in accordance with tolerance Hp-0.5 V)
- Mobile phones in the state of OFF, and press the button on
- If the current (amperage) in a digital ampere dipower supply pointer when the button is pressed on, it just means there's still a problem on its hardware (HW), it is necessary to check the components on / off until the battery.
- When the ampere when the button is pressed on, up about? 50 mA, then the problem that occurs is a matter of software (SW), then you need to do is re-programmed HP (flash) or program is upgraded to higher versions.
b. Total death from falls.
Handling:
- HP may not be tested by using the power supply, but HP should be dismantled first, heated, and repositioned back to the location / position of the components has changed as a result of HP fell.
- After that, the new HP using the power supply should be tested to determine damage to the Hardware (HW) / Software (SW).
- Most likely a damaged components as a result of the fall is the HP PA IC / IC Power.
c. Total death due to hit the water.
Handling:
- For taxable HP water is also the first time should not be tested by using the power supply, because the risk of short circuit occurs between the components in water, but must first HP divakum, heated, or by first diblower given IPA cleaning liquid, can also use the grain silica to absorb the water that existed at HP.
- After HP confirmed it was dry, then we should use the power supply to determine the damage occurred on the Hardware (HW) or Software (SW).
- At HP's exposed to water, usually there is damage to HPnya accessories.
2. Total die because of IC phone UI.
In HP's case like this then requires test equipment that is power supply.
The steps are as follows:
- Connect the power supply on the phone, give the voltage (volts) equal to 3.6 V (or in accordance with tolerance Hp-0.5 V)
- At the time the phone is in off state, refer to the power supply needles amperes will increase by 100mA.
- The phone will start, LED lights, VIBRA vibrate.
Handling:
- Remove the IC UI, then turn on the phone.
- Then there is the display on the LCD mobile phone "Insert SIM Card".
- Put new IC UI.
- Turn on the phone, the phone will work fine.
3. Total dead cell phone because the CPU IC.
To determine whether the cell phone because the IC die total CPU is as follows:
- Give the voltage (volts) on the phone by using the power supply of 3.6 V (or in accordance with tolerance Hp-0.5 V).
- At the time the phone is not turned on, the needle ampere silent, but if the phone is switched on then the needle will rise 100mA amperes.
Handling:
- If the IC CPU is still in good condition, then we only need to heat the IC CPU by using a blower, but if the CPU IC is damaged, then we need to replace with a new CPU IC. Before we replace our CPU IC must first have the anti-hot glue and liquid glue crusher anti-heat, because the CPU IC is protected by anti-heat glue, after we destroy the anti-hot glue, then we can heat (blower) CPU IC for a new replacement. Similarly, after we replace it with a new CPU IC then we need to give more anti hot glue to protect the new CPU IC we replace it.
4. Total dead cell phone when we call.
For testing we use the power supply by way of:
- Connect the phone with power supply, give the voltage (volts) equal to 3.6 V (or in accordance with tolerance Hp-0.5 V) on the phone.
- Needles amperes will not move when the phone is still in a state of death.
- We turn on the phone and then used to make calls, then the needle will show the number of amperes above 400mA.
Handling:
- Replace with a new IC PA, after re-testing was done as above, if the needle test results show the figures below 400mA amperes, the phone is in good condition. | |
|   | |
| Author | Message |
|---|
FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Mon Sep 27, 2010 12:23 pm Mon Sep 27, 2010 12:23 pm | |
| Learn How To Make Solutions by Schematic Reading
Vio = 1.8v (galing sa UEM to CPU)
Vana = 2.8v (galing sa UEM to UEM)
Vcore = 1.4v (galing sa UEM to CPU)
Vr3 = 2.8 v (galing sa UEM to RF Ic or Oscilator 26Mhz)
Purx = 1.8v (galing sa UEM to CPU)
Sleepx = 1.8v (galing sa CPU to UEM)
Sleep Clock = 32.768khz (Galing sa oscilator 32.768 to UEM to CPU)
Rf Clock = 26Mhz (Galing sa oscilator 26Mhz to RF Ic to CPU) | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Mon Sep 27, 2010 12:25 pm Mon Sep 27, 2010 12:25 pm | |
| Configuring email for Nokia N97 Yahoo account Settings Incoming e-mail:
- username: your email address
- password: your password
- Incoming mail server: pop.mail.yahoo.fr
- access point used: sl2sfr
- Account type: POP3
- Security: SSL / TLS
- Port: 995
- APOP secure login: Enabled
Outgoing e-mail:
- username: my email address
- password: my password
- Outgoing mail server: smtp.mail.yahoo.fr
- access point used: sl2sfr
- Security: SSL / TLS
- Port: 465
Hotmail Account Settings Incoming e-mail:
- username: my email address
- password: my password
- Incoming mail server: pop3.live.com
- access point used: sl2sfr
- account type: POP3
- security: ssl / tls
- Port: Default
- APOP secure login: disabled
Outgoing e-mail:
- username: your email address
- password: your password
- Outgoing mail server: smtp.live.com
- access point used: sl2sfr
- Safety: starttls
- Port: Default
After the step above , simply configure "user settings", "parameters of recovery" and "automatic connection" according to your preferences. | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Mon Sep 27, 2010 12:25 pm Mon Sep 27, 2010 12:25 pm | |
| | |
|   | | nighthawk
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 68
Job/hobbies : RETIRED....
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Wed Sep 29, 2010 8:41 am Wed Sep 29, 2010 8:41 am | |
| very informative post, we can learn a lot from this post if we read and study it
glad to know that we have this kind of post in this forum
regards:
PS: suggestion to admin,
Pls put this thread on HOT THREAD | |
|   | | AAPTEK
FOUNDER & ADMIN



Age : 68
Job/hobbies : Instructor, Programmer& Technician
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Wed Sep 29, 2010 11:07 am Wed Sep 29, 2010 11:07 am | |
| firstlly i big thanks to my bro FULLFLASHGSM
Hi to all aaptek admin, seniors and advance member
Say thanks to him for the mega thread 2010
mega thread
hot thread
stcky thread
globel annuoncement theread
----------------------------------
thanks a lot the power full thresd
regards | |
|   | | master_mudieee
JUNIOR ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : technician
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Wed Sep 29, 2010 11:17 am Wed Sep 29, 2010 11:17 am | |
| | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Wed Sep 29, 2010 7:45 pm Wed Sep 29, 2010 7:45 pm | |
| - nighthawk wrote:
- very informative post, we can learn a lot from this post if we read and study it
glad to know that we have this kind of post in this forum
regards:
PS: suggestion to admin,
Pls put this thread on HOT THREAD thanks brother. i hope all good information for aaptek student.learn and study . thanks again dear. | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Wed Sep 29, 2010 7:48 pm Wed Sep 29, 2010 7:48 pm | |
| - AAPTEK TEAM wrote:
- firstlly i big thanks to my bro FULLFLASHGSM
Hi to all aaptek admin, seniors and advance member
Say thanks to him for the mega thread 2010
mega thread
hot thread
stcky thread
globel annuoncement theread
----------------------------------
thanks a lot the power full thresd
regards thanks dear brother. inshallah more i post usedful thread for student. ur bro | |
|   | | AAPTEK
FOUNDER & ADMIN



Age : 68
Job/hobbies : Instructor, Programmer& Technician
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Wed Sep 29, 2010 9:52 pm Wed Sep 29, 2010 9:52 pm | |
| - nighthawk wrote:
- very informative post, we can learn a lot from this post if we read and study it
glad to know that we have this kind of post in this forum
regards:
PS: suggestion to admin,
Pls put this thread on HOT THREAD thanks for the co-op with aaptek and good opinion !! | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 5:20 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 5:20 pm | |
| Nokia Bb5 Contact Service Problem Reason & solution.
SX4: SX4 Smart Card, is a tool or method which is developed by Nokia to
write some data protection for a specific area in EEPROM is useful for
preventing modification of the data.
When SX4 PROCESS is Required ?
In the case of a loss (data corrupt) data charging (not charging), data
network (no network). Dll.RF calibration calibration-charging.
So, all these problems caused by mistakes in the process of flashing or after
write RPL or erase process is done in a certain area
HOW DO I KNOW THAT MY PHONE PROCESS SX4 needs to be done?
- When the phone appears CONTACT SERVICE, CONTACT retailers, NOT
charging after flashing, no network, etc. When the SELF TEST is done by
using the box like JAF repair, etc. will be obtained is the result of failed "ST_SECURITY_TEST Failed"
How do I make a SX4?
- Plug the phone in the repair box (JAF, MTBOX, MXKEY, etc.)
Write pm area with 309 results read from the normal mobile phone or can
also write FULL PM area without 308 (SIMLOCK area).
What to do sx4 without internet connection?
-sure Certificate damaged area musti made first with the FLASH erase, or
write RPL blank
Reset NPC (when using mxkey)
What is a Certificate Area?
Press info on the box like JAF flasher, etc. and see the results LOG ...
This is an example of the correct Certificate
Default SN type:
Code:
IMEI plain: 351862xxxxxxxxxxIMEI spare to net: 3A 15 68 02 01 23 60 03IMEI SV to net: 33 15 68 02 01 23 60 03 F6LOCK STATUS:Config KEY: 0000000000000000Provider KEY: 2440700000000000Provider: AT &T; U.S.A. (3650)Key Code count: 0, FBUS Code count: 0Block 1:Lock 1: OPEN Lock 2: OPEN Lock 3: OPEN Lock 4: OPEN Lock 5: OPENBlock 2: Lock 1: OPEN Lock 2: OPEN Lock 3: OPEN Lock 4: OPEN Lock 5: OPEN Block 3: Lock 1: OPEN Lock 2: OPEN Lock 3: OPEN Lock 4: OPEN Lock 5: OPEN Block 4: Lock 1: OPEN Lock 2: OPEN Lock 3: OPEN Lock 4: OPEN Lock 5: OPEN Block 5: Lock 1: OPEN Lock 2: OPEN Lock 3: OPEN Lock 4: OPEN Lock 5: OPEN Block 6: Lock 1: OPEN Lock 2: OPEN Lock 3: OPEN Lock 4: OPEN Lock 5: OPEN Block 7: Lock 1: OPEN Lock 2: OPEN Lock 3: OPEN Lock 4: OPEN Lock 5: OPEN
This is an example Certificate of damaged:
Default SN type:
Code:
IMEI plain: 123456765321?LOCK STATUS:Config KEY: fffffffffffffffffffffffProvider KEY: fffffffffffffffffffffProvider: UnknownKey Code count: 0, FBUS Code count: 0Block 1: Lock 1: CLOSED
BB5 Contact Service, Restart Problem,How To Erase BB5, Restore PM and RPL Backup!!!
I saw here many times peoples are having with this "Contact Service or Provider" problem
and also unable to Write or Restore the Orignal backup to the Phone. just follow and learned how to repair BB5 Contact Service/Retailer, how to erase BB5 and Restore PM and RPL Backup!!! Now we shall more reflect upon this matter;- How To Remove Contact Service or Provider ?
Firstly we should get Phone Info and see Imei and SL (Sim Lock) Zone are damaged or Not.Get Phone Info:
In Case when you got Damaged Imei: 123456789012345 and you dont have Orignal RPL Backup
then free way is try to solve this problem by downgrading if Imei and SP Data is still damage,
then Upgrade it back and you must need to buy an new RPL to fix this problem. Use ASK to RPL Service.
In Case when Phone Imei is oK but Only SL Zone is damaged and you don't have Orignal PM 308 backup then wat to do.If Courpted SP Data looks like this below:
CONFIG KEY: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
PROVIDER KEY: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
Provider: Unknown provider
And phone is supported for Unlocking, then you can try to Repair it free with any BB5 Unlocker by Unlock Button or with Repair SP Data Option. (It should Repair) Otherewise you may need to New RPL.
And If Courpted SP Data looks like this:
CONFIG KEY: 0000000000000000
PROVIDER KEY: 0000000000000000
Provider: Unknown provide
Then you must need to buy an New RPL whether Phone is supported with any BB5 Unlocker.
We can not Repair it free, Use Ask To Rpl Service.In Case when you have RPL Backup and have not PM 308, you can only Restore the Phone Imei but you can not Repair the Courpted SP Data like this: PROVIDER KEY: 0000000000000000,
Provider: Unknown provide In Case when you have PM 308 backup and have not RPL, you can Repair SP Data but you can not Repair Phone Imei by only PM 308 backup. Use ASK To RPL Service.
In Case when Phone Imei and SL Zone both are OK but phone is still on Contact
Service/Provider.
First take Self Test and check ST Security Test is Passed or Failed?
If Passed then do File System Formate and after that make Factory Setting and see problem is
solved or not, if still same then check phone hardware.
And if ST Security Test is Failed then Write PM Field [1] And [309] as stanner said,
(or full pm as you wish) by using SX4 Auth Service and after that make Factory Setting.
Oftenly Phone can Repair by Downgrading and Writing RPL.
Then Write PM With SX4 if same then Update back and See problem is Solved or not.
(It should work now!) otherwise try to repair it by erasing method.
How To Remove Restart Problem when Phone Imei is oK but Phone goes to Restart or Shut Off after a while!
In this case first try to solve this problem by only Write Full Modified (Without 308 Field) PM With
SX4 Auth.Use SX4 and when it done Successfully then immediately Write supported full modified PM to the phone and check phone without MMC, problem is fixed or not, if not then Full Flash and after that Write PM with SX4, or try to solve
by Downgrading.Oftenly Restart problem is removed by only do File System Format and Factory Default. (Check
phone without MMC) Otherwise there is only one way is left to Repair it with Software and that
is Erase Flash (Rap), to start the Erasing Procedure,
Follow this given below Method:
Before Start Erasing Flash, Save your both backup PM 308 and RPL backup (CRT 308 and CRT
BKP)If you are going to do erase newer BB5 + (Plus) Phone then you must Save also Full PM 0 to 400
Backup, coz you will need it for restore the orignal field 308, this is really fast easy and perfect
way to restore the PM 308 Field, otherwise you may need to buy an new RPL.So be careful. . .
Now we are ready to do erase.Select UNI_rapido.bin in Mcu Part and click to Flash
and for MT Select uni_rap.bin as MCU.
when phone will fully erased then Phone Imei will be: 12345610654321, SP Area will damaged
and CMT Flash Data will shown: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
Now Full flash with any Firmware ver but selected firmware should be not too Old or too New,
coz we may need it in another case.After Flash when phone will turn On, you will get
damaged IMEI: 12345610654321 and Courpted SP Area:
PROVIDER KEY: 0000000000000000, Provider: Unknown provide
Now first of all you have to Restore the Orignal backup of PM 308, in case when you are unable
to restore the PM 308 backup then flash again with same FW when you were take backup.
When it flash successfully then plz stay a min and write it (PM 308) back to the phone, now
Disconnect phone, connect it again and see SL Zone is Repaired or Not.
(It should be repair now), if not then flash again with same FW and restore the PM 308 backup.
But if you have Full PM 0-400 backup then no need to Flash again, just Write it (Full PM 0-400
backup) back to the phone without SX4,when it done successfully then remove cable to the box,
replug cable and get info you will see SP Area is Repaired now, if not then it will be repair after
writing RPL backup.
After successfully restore the PM 308 backup phone will on Contact Service/Retailers or full
working phone with damaged Imei. In this condition when phone has damaged Imei:
12345610654321 you can write full modified PM
(without 308 field) without using SX4, coz phone has not certificate (IMEI), therefor no need to
use SX4.Now we have to Restore RPL backup. If you are using JAF then Click on CRT Tool, now you will
See BB5 Certificate Tool Window:
tick on Write RPL Option and also mark on Plain RPL box, now Select your RPL backup and
click on Write RPL button.Get info now and see Imei is restored succcessfully or not phone
should be on Contact Service/Retailer or fully working. . .
But if you are failed to restore the RPL backup, i mean phone Imei is still damage and phone
show only Nokia and then shut Off in case now you Write blank_rpl and Flash again with Latest Firm Ware.
When it (flash process) done successfully then write RPL backup, get Info and see Imei is back or
not, it (Imei) should back now, and your Phone will on Contact Service/Retailer, if Not and you
got dead phone Please follow again all above erasing method.
Finally use SX4 and Write PM Field [1] and [309] (or full pm as you wish), now we have done all
abt Software.I think That's all. . . abt BB5 Repair with Erasing Method and we have confirmed
now, phone has Software Problem or not.
| |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 5:30 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 5:30 pm | |
| MOBILE HARDWARE & SOFTWARE (PDF Urdu)
Introduction to Mobile
Difference between Mobile Hardware and Software
Mobile Hardware
Mobile Software
Classification of Mobile
AMPS Mobile Models
GSM Mobile Models
Mobile Communication System Diagram
Difference between AMPS and GSM Mobiles
SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) Card
WIM (Wireless Identity Module)
Mobile Phone Locks
Code:
http://www.4shared.com/file/187982957/84681983/Mobile.html | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 5:39 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 5:39 pm | |
| How to prevent viruses phone
1. Suspect in case of strangeness on your mobile phone.
The emergence of unusual format2x weird who you see when you receive SMS and incoming calls should not you receive. Turn off the phone, then switch back to refuse shipment viruses.
2. Be careful if you want to write your phone number service Internet, the sender could be a virus doing random spread of the virus.
3. Back up your data regularly. at least once a month you can do on your pc sinkronice either phone book data, e-mail or a simple lainnya.Tips this roundabout will save the data from virus threats.
4. If you use the smartphone supported applying the window & it's good JAVA program with anti virus up date, because after all pairs with the same OS on your pc then the probability that a virus similar magnitude.
5. Be very careful before running the new application program downloaded from the Internet, especially for mobile smartphones.
6. If you frequently use email services on mobile phones be careful in opening attadment executable file, need to remember phone virus originally came from an email message sent via SMS.
VIRUS FACT
Be careful to receive calls that screen appears: XXX, YYY, 000.123. If the view should not be accepted let alone to complete (data, CNN: 2000, location: Asia, Europe).
Screen = ACE, Unavailable. Do not answer it (data, Symantec: 2001 to the present, location: asia, europe, U.S.)
Devoted nokia virus sms serie 3300 & 3360 series flat form. (Symbian & J2ME / MIDP) found in Job de Haas & # 8220, ITSX & # 8221, message on the dangers advantage of a bug that three types of mobile phones. (Data: Nokia.com, location: United States, southeast Asia)
Virus sms Johan Haan Dylan's creation in 2002 disseminated through the Internet, as it is now active. Mid-2003 there was a group of DYKENVIRUS-MAKER develop MMS & Java virus via OTA: do not receive an sms form %@#<<>* (no text message receive). This is an indication the virus is sent. (Data: Service Center, 2004, location : southeast Asia).
SCU: Anti - Virus information
Veto - unwanted Messages
PIRATOS - HACKER, THE SERVER
SMS dispatcher
Created Virus Nokia Mobile Which Deplete
Be careful receive messages Short message service (SMS), especially when using Cellular Phone (Mobile) Nokia type 3310, 3330 and 6210.Pasalnya, a computer security researchers in the Netherlands succeeded in creating a mobile phone viruses that can damage these Nokia phones.
Similarly, as reported BBC.co.uk.
Exchanging SMS messages currently popular among GSM-based mobile phone users. Because, in addition to cheap, fixed SMS recipients can receive messages on his cell phone was not even active or are beyond the reach of the signal operator.
However, if you use a Nokia mobile phone type of 3310.3330 and 6210, so be careful when receiving an SMS message. Section, a computer security researchers in the Netherlands succeeded in creating cell phone viruses that can damage these Nokia phones via SMS.
This virus was created by Job de Haas, a researcher at security research company ITSX. This dangerous message, utilizing existing bug on three types of mobile phone. When it was received, the virus that will make some handsets which can not be used at all.
Accordingly, the SMS facility is designed to automatically activate existing functions in a mobile phone via a script that is sent by mobile phone operators.
Mobile phone users are not able to read the script, but the handset will receive it as a command to activate certain features. Such script is used by De Haas to create these mobile viruses.
Vendor Nokia claims to have fix the bug that existed at the type of the mobile phone. But according to De Haas, a few old phone of this type still has a bug that can be used by the virus creations. | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 5:49 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 5:49 pm | |
| 10 Things you don't know about NOKIA
10 Things you don't know about NOKIA
1) The ringtone "Nokia tune" is actually based on a 19th century guitar work named "Gran Vals" by Spanish musician Francisco Tárrega. The Nokia Tune was originally named "Grande Valse" on Nokia phones but was changed to "Nokia Tune" around 1998 when it became so well known that people referred to it as the "Nokia Tune."
2) The world's first commercial GSM call was made in 1991 in Helsinki over a Nokia-supplied network, by Prime Minister of Finland Harri Holkeri, using a Nokia phone.
3) Nokia is currently the world's largest digital camera manufacturer, as the sales of its camera-equipped mobile phones have exceeded those of any conventional camera manufacturer.
4) The "Special" tone available to users of Nokia phones when receiving SMS (text messages) is actually Morse code for "SMS". Similarly, the "Ascending" SMS tone is Morse code for "Connecting People," Nokia's slogan. The "Standard" SMS tone is Morse code for "M" (Message).
5) The Nokia corporate font (typeface) is the AgfaMonotype Nokia Sans font, originally designed by Eric Spiekermann. Its mobile phone User's Guides Nokia mostly used the Agfa Rotis Sans font.
6) In Asia, the digit 4 never appears in any Nokia handset model number, because 4 is considered unlucky in many parts of Southeast/East Asia.
7) Nokia was listed as the 20th most admirable company worldwide in Fortune's list of 2006 (1st in network communications, 4th non-US company).
8. Unlike other modern day handsets, Nokia phones do not automatically start the call timer when the call is connected, but start it when the call is initiated. (Except for Series 60 based handsets like the Nokia 6600)
9) Nokia is sometimes called aikon (Nokia backwards) by non-Nokia mobile phone users and by mobile software developers, because "aikon" is used in various SDK software packages, including Nokia's own Symbian S60 SDK.
10) The name of the town of Nokia originated from the river which flowed through the town. The river itself, Nokianvirta, was named after the old Finnish word originally meaning sable, later pine marten. A species of this small, black-furred predatory animal was once found in the region, but it is now extinct. | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 5:52 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 5:52 pm | |
| Modify RJ45 Comport for any type of Phone C261, some ODM Nokia..  DKU-5, CA-42.. 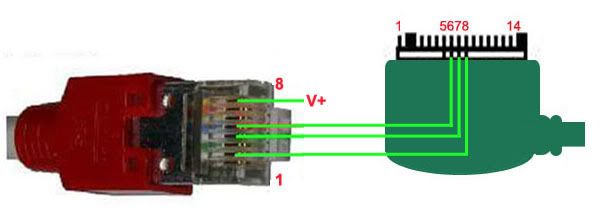 Siemens C55 and similar model..  SE J100 and similar models..  1255  Motorola V680..  Huawei C2601..  | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 5:59 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 5:59 pm | |
| | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:01 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:01 pm | |
| Using a Volt Meter Multitester
1. Connect the black wire to the COM (Ground), and attach the Red cable to the far right hole (V / Ohm).
2. Determine the measurement object, for example, will measure battere Nokia distinguished capacity 3.7 V.
3. See scale on Multitester pd part V (Volt), there are two, namely:
DC Volt - (Voltage unidirectional): Battery Voltage, TEG. Output IC Power, etc. (There is a polarity and -)
~ Volt AC (Alternating Reverse Voltage): Voltage PLN, and the like.
Generally in use in the measurement of weak currents, such as measurement of cell phones, etc. The selected distinguished Volt DC -
Once selected the DC volt scale, there is a distinguished value2 Volt DC listed to the tsb. Example:
200mV which means it will measure the voltage of 0.2 volts maximum
2V which means it will measure the voltage of maximum 2 Volt
20V which means it will measure the voltage of 20 volts max
200V which means it will measure the maximum voltage 200V
750v which means it will measure voltage 750v max
Use the nail on the scale for measurement, eg 3.6 Volt Battery using a scale on the 20V. So the result will be accurate eg read: 3.76 Volt.
If using a scale of 2 V is shown figure 1 (a sign of overload / over the scale)
If using a 200V scale will read a non-accurate results but eg read: 3.6 V or 3.7 V SJA (1digit behind the comma)
If using 750v but the results can be unreadable kaan 3 or 4 volts (Rounded lsg without commas)
After the object is measured sdh, sdh scale selected and auspicious, then take the measurement with the red to the positive paste rev battere and black wire to negative battery. It would appear the measurement results.
If the cable is reversed the result will still appear, but there is a negative sign in front of the result. Differences with Analogue Multitester. If the rev needle will be stuck upside left.
NB: if there Multitester DH keys, means Data Hold. If pressed then it will freeze, and can note the results. | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:02 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:02 pm | |
| Using Digital Multitester as Estimator Line (Continuity)
1. Select Scale Buzzer, imaginable Sound icon or any of his LEDs. If the red and black wires attached tester lsg, it will sound signal path Multitester OK. Without barriers (<50 Ohm).
2. Select the object of measurement. Eg will measure the path of Power ON UEM IC Q7 feet to Switch On-off. Paste one of the wires (which aja free) to ON Off Switch legs, one leg longer to UEM IC P7 or capacitor closest. If the sound is a sign of a good track and connected. If no sound, try sdh true whether the location of measurement. If sdh, broken lines and must be ascertained in the jumpers. | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:04 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:04 pm | |
| Using Digital Multitester as a measure of the flow circuit
1. Move the red wire to the 20A. And black wires remain in COM (ground). Selected holes 20A as it would measure currents reply> 0.2 A.
For example, will measure the charging current battere. One way to include one of the charger cable is cut. And cable attached to a red wire and black wire Multitester. Perform measurements when the phone dicharger. For example, the value of which contained 0.725 mean 0.725 A charging current of 725 mA alais.
Or revoke Fuses (Fuse) and then paste it into rev pole fuse PCB pd. Then measure the results.
Measuring Lithium Battery Original or False.
1. Red cable is fixed at 20A, black rev at GND.
2. Scale fixed at 20A
3. Paste Red Battery Cable
4. Paste black rev - Battery
5. see results emerged:
If reflexively, pointed to a specific number and return to Zero, a sign of genuine Lithium Battery.
If the results point to a specific number, and stable. Lithium Batteries false omen, and cept2 unplug from Battery rev. Because the batteries will be hot .. because didalamya cut no controlling IC circuit.
For the original lithium batteries, although the rev taped on to the batteries, non-issue ...
So often the hot cell phone or even explode when dicharging. Because use of Lithium Battery false. There are non-controlling IC circuit. So when the battery Fully. Sensor BTEMP not work. So who has a full battery will continue to be filled so that they will be hot hot and eventually resulted kerusakanpada interchangeable cell phone, or even could have become bloated da interchangeable battery to explode.
By Karen was always use an original reply Lithium Battery which contains short circuit inside the IC controller. | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:06 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:06 pm | |
| Master TOOL BOX Video
 Our purpose POWER WITH MASTER BOX (A simple and applied tool for any mobile phone maintainer ) In actual fact, It is unnecessary to know what the mobile model is (VKCSPICE - ZTE- FLY- HAIER- Huawei- Cect- Anycool- TCL etc.), nevertheless there are just two things we should realize. 1. CPU type (6205-6217-6218-6219-6226-6227-6228-6229-6225-6223-6230..) (6600D-6600M-6600E-6600I-6600H-6600R-6800-......) etc. 2. Flash type (NOR+PSRAM -NAND) We support more than 100 different types of flash. Master box is a box-tool for maintaining mobiles, which you can trust and depend on to search Pin-Out of your mobile phone ( usb port & C com port ) Before releasing Master Box, we have spent much time for researching and doing a hard work for testing the box with more than 1000 different mobiles, which have different CPUs and flash types (MTK , SPD Spreadtrum, TI Texas Instrument, Skyworks, AD Analog Device, Infineon). WHY WE NAMED IT AS "MASTER BOX"? 1- As it is the master in hardware, the box engine is FPGA ATMEGA, which makes it having a long working life, and much lower fault in pinout searching. 2- As we have applied our perfect design and competent technical work with FPGA, the box now is the master in the fastest pinout searching. Searching time for usb port (SPD etc.) - 1 to 20 seconds; Searching time for COM port (MTK, SkyWorks etc.) - 2 to 30 seconds). 3- As it is the master in hardware protection, the Box and mobiles have been protected by short circuit and 'positive to negative' connections.. 4- As it is the master in flashing, the box supports more than 100 types of flash ICs. 5- As it is the master in software protection, our software has been protected by smartcard dongle with good security system. 6- As it is the master in detection. RX TX GND- VCC, D+ D- 7- As it is the master in support and update. Master box package 1- Masterbox 2- Full Cable Set (33 connectors) for most models in the market 3- Smartcard dongle 4- Dongle upgrade client http://rapidshare.com/files/388411147/Master_TOOL_BOX_Video_By_STBSL.rarhttp://hotfile.com/dl/43378260/e1168a1/Master_TOOL_BOX_Video_By_STBSL.rar.html | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:09 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:09 pm | |
| | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:12 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:12 pm | |
| | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:13 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:13 pm | |
| tutorial t-box
Code:
http://www.4shared.com/file/v9Cr5uFk/TUTORIAL_T-BOX.html | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:15 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:15 pm | |
| video UCT Box installation .exe
Code:
http://www.4shared.com/file/q42nrDHo/uct_installation_box.html | |
|   | | FULLFLASHGSM
THE GREAT ADMIN



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : www.apptekgsm.com
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:18 pm Thu Sep 30, 2010 6:18 pm | |
| | |
|   | | kladeed
AMCT STUDENT



Age : 33
Job/hobbies : student
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Tue Oct 05, 2010 2:24 pm Tue Oct 05, 2010 2:24 pm | |
| wow great news effort sir, thanks a lot | |
|   | | kerryzeng
NEW MEMBER



Age : 37
Job/hobbies : internet
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Wed Jan 26, 2011 12:19 pm Wed Jan 26, 2011 12:19 pm | |
| | |
|   | | BONUO CELL ™
AMCT SUPERIOR ADMIN


Age : 44
Job/hobbies : Web Design And Programers
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Wed Jan 26, 2011 9:06 pm Wed Jan 26, 2011 9:06 pm | |
| | |
|   | | sansam
AMCT MEMBER



Age : 36
Job/hobbies : admin
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Sat Jun 11, 2011 10:21 am Sat Jun 11, 2011 10:21 am | |
| - FULLFLASHGSM wrote:
- EEPROM
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
EFR
Enhanced Full Rate; a alternative voice codec that provides improved voice quality in a GSM network (see codec)
EFT
Electronic Funds Transfer
EGSM
Extended (frequency range) GSM
EIR
Equipment Identity Register; a database that contains a list of all valid mobile stations within a network based on their IMEI
EIRP
Effective Isotropic Radiated Power
EPOC
The mobile phone operating system developed by Symbian. Derived from epoch-the beginning of an era-EPOC is a 32-bit operating environment which comprises a suite of applications, customisable user interfaces, connectivity options and a range of development tools
EPROM
Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
Erlang
A dimensionless unit of average traffic density in a telecommunications network
ERMES
Enhanced Radio Messaging System; a paging technology developed by ETSI which was intended to allow users to roam throughout Europe. Adopted by a number of European and Middle Eastern countries, ERMES, like paging in general, was overtaken by the ubiquity of GSM
ERO
European Radiocommunications Office
ERP
Effective Radiated Power
ESMR
Enhanced Special Mobile Radio; a US PMR variant (see SMR)
ESN
Electronic Serial Number; a 32-bit number that uniquely identifies a mobile phone
ESPRIT
European Strategic Programme for Research and Development in Information Technology
ETACS
Extended TACS; the extension of TACS by the addition of new frequencies
ETS
European Telecommunications Standard
ETSI
European Telecommunications Standards Institute: The European group responsible for defining telecommunications standards
FACCH
Fast Associated Control Channel; similar to the SDCCH but used in parallel for operation of the TCH. If the data rate of the SACCH is insufficient borrowing mode is used
FB
Frequency Correction Burst; used for frequency synchronisation of the mobile
FCC
Federal Communications Commission; the US regulatory body for telecommunications
FCCH
Frequency Correction Channel; downlink only, correction of MS frequencies, transmission of frequency standard to MS etc.
FDD
Frequency Division Duplex; a radio technique which uses paired spectrum; UMTS has an FDD element
FDMA
Frequency Division Multiple Access-a transmission technique where the assigned frequency band for a network is divided into sub-bands which are allocated to a subscriber for the duration of their calls
FEC
Forward Error Correction
FH
Frequency Hopping
FH-CDMA
Frequency Hopping CDMA
FMC
Fixed Mobile Convergence
FMI
Fixed Mobile Integration
FPLMTS
Future Public Land Mobile Telecommunications System, the original title of the ITU third generation concept now known as IMT-2000
FRA
Fixed Radio Access; see WLL
FSDPSK
Filtered Symmetric Differential Phase Shift Keying
FSK
Frequency Shift Keying; a method of using frequency modulation to send digital information
FSOQ
Frequency Shift Offset Quadrature Modulation
FSS
Fixed Satellite ServiceGb
The interface between the PCU and the SGSN in a GSM/GPRS network
Gc
The interface between the GGSN and the HLR in a GSM/GPRS network
Gd
The interface between the SGSN and the SMSC in a GSM/GPRS network
Gf
The interface between the SGSN and the EIR in a GSM/GPRS network
Gi
The interface between the GGSN and the Internet in a GPRS network
Gn
The interface between the GGSN and the SGSN in a GPRS network
Gp
The interfaces between the GGSN/SGSN and the Border Gateway in a GPRS network
Gr
The interface between the SGSN and the HLR in a GPRS network
Gs
The interface between the SGSN and the MSC in a GSM/GPRS network
GAIT
GSM/ANSI 136 Interoperability Committee
GAP
Generic Access Profile; a DECT term
Gbit/s
A unit of data transmission rate equal to one billion bits per second
GMSC
Gateway Mobile Services Switching Centre; the gateway between two networks
GCF
Global Certification Forum
Geostationary
Refers to a satellite in equatorial orbit above the earth which appears from the surface to be stationary
GERAN
GSM-EDGE Radio Access Network; the name for the evolution of GSM towards 3G based on EDGE
GGRF
GSM Global Roaming Forum
GGSN
Gateway GPRS Support Node; the gateway between a cellular network and a IP network.
GHz
A unit of frequency equal to one billion Hertz per second
GMPCS
Global Mobile Personal Communications by Satellite
GMSK
Gaussian filtered Minimum Shift Keying; a refinement of FSK which minimises adjacent channel interference
GPRS
General Packet Radio Service; standardised as part of GSM Phase 2+, GPRS represents the first implementation of packet switching within GSM, which is a circuit switched technology. GPRS offers theoretical data speeds of up to 115kbit/s using multislot techniques. GPRS is an essential precursor for 3G as it introduces the packet switched core required for UMTS
GPS
Global Positioning System; a location system based on a constellation of US Department of Defence satellites. Depending on the number of satellites visible to the user can provide accuracies down to tens of metres. Now being incorporated as a key feature in an increasing number of handsets
GRX
GPRS Roaming Exchange
GSM
Global System for Mobile communications, the second generation digital technology originally developed for Europe but which now has in excess of 71 per cent of the world market. Initially developed for operation in the 900MHz band and subsequently modified for the 850, 1800 and 1900MHz bands. GSM originally stood for Groupe Speciale Mobile, the CEPT committee which began the GSM standardisation process
GSM MoU
The GSM Memorandum of Understanding, an agreement signed between all the major European operators to work together to promote GSM. The precursor of the GSM Association
GSM-R
GSM-Railway, A variant of GSM designed to meet the special communications needs of international train operators
Handoff
The transfer of control of a cellular phone call in progress from one cell to another, without any discontinuity
Hands-free
The operation of a cellular phone without using the handset; usually installed in vehicles.
HCS
Hierarchical Cell Structure; the architecture of a multi-layered cellular network where subscribers are handed over from the macro to the micro to the pico layer depending on the current network capacity and the needs of the subscriber
HDLC
High level Data Link Control
HIPERLAN
High Performance Radio Local Access Network; a wireless local area network being standardised by ETSI (Also HIPERLAN2)
HLR
Home Location Register; the database within a GSM network which stores all the subscriber data. An important element in the roaming process
HSCSD
High Speed Circuit Switched Data; a special mode in GSM networks which provides higher data throughput By cocatenating a number of timeslots, each delivering 14.4kbit/s, much higher data speeds can be achieved
HSPSD
High Speed Packet Switched DataIub
The interface between the Node B and the RNC in a UMTS network
Iur
The interface between RNCs in a UMTS network
Iups
The connection between the RNC and the packet switched network in a GSM/GPRS/UMTS network
Iucs
The connection between the RNC and the circuit switched network in a GSM/GPRS/
UMTS network
I-ETS
Interim European Telecommunications Standard
I-mode
A service developed by Japanese operator NTT DoCoMo, I-mode delivers a huge range of services to subscribers and has proved enormously popular with some 30 million regular users. The revenue sharing model used for I-mode is being adopted by other operators as the basis for the new services enabled by GPRS and 3G
IMEI
International Mobile Equipment Identity
IMSI
International Mobile Subscriber Identity; an internal subscriber identity used only by the network
IMT-2000
The family of third generation technologies approved by the ITU. There are five members of the family: IMT-DS, a direct sequence WCDMA FDD solution IMT-TC, a WCDMA TDD solution IMT-MC, a multicarrier solution developed from cdma2000 IMT-SC, a single carrier solution developed from IS-136/UWC-136 IMT-FT, a TDMA/TDD solution derived from DECT
IN
Intelligent Network
INAP
Intelligent Network Application Part
Internet
A loose confederation of autonomous databases and networks. Originally developed for academic use the Internet is now a global structure of millions of sites accessible by anyone
Intranet
A private network which utilises the same techniques as the Internet but is accessible only by authorised users
IP
Internet Protocol
IPR
Intellectual Property Rights
IPv6
The next generation of IP addressing designed to replace the current system IPv4 which uses a 32 bit address code which limits the number of possible addresses. IPv6 uses a 128 bit code ensuring that the possible number of IP addresses will be virtually limitless
IrDA
Infra red Data Association
Iridium
A low earth orbit satellite communications system developed initially by Motorola.
IS-54
The first evolution in the USA from analogue to digital technology. Used a hybrid of analogue and digital technology, superseded by IS-136
IS-95
Cellular standard know also as cdmaOne
IS-136
Cellular standard also known as TDMA or D-AMPS
ISDN
Integrated Services Digital Network
ISO
International Standards Organisation
ISP
Internet Service Provider
ITU
International Telecommunications Union
ITU-R
ITU Telecommunications Radio Sector
ITU-T
ITU Telecommunications Standardisation Sector
IWF
Interworking Function
Java
A programming language developed by Sun Microsystems Java is characterised by the fact that programs written in Java do not rely on an operating system
JPEG
Joint Photographic Experts Group
LAN
Local Area Network
LANS
Local Area Network Services
LAP
Link Access Protocol
LEO
Low Earth Orbit; refers to satellites which orbit the Earth at around 1,000 kilometres
LMSS
Land Mobile Satellite Service
LOS
Line of Sight
MAC
Media Access Control; the lower sublayer of the OSI system
MAN
Metropolitan Area Network
MAP
Mobile Application Part
Mbit/s
Megabit: a unit of data transmission speed equal to one million bits per second
MHz
Megahertz; a unit of frequency equal to one million Hertz
MCPA
Multi Carrier Power Amplifier
MeXe
Mobile Execution Environment; likely to be based on Java, MeXe enables WAP-enabled devices to offer a wider range of features with greater security and flexibility, as well as greater control of telephony features
MFSK
Multiple Frequency Shift Keying
MMI
Man Machine Interface
MMS
Multimedia Messaging Service; an evolution of SMS, MMS goes beyond text messaging offering various kinds of multimedia content including images, audio and video clips
MMSK
Modified Minimum Shift Keying
MNO
Mobile Network Operator
Modulation
The process of imposing an information signal on a carrier. This can be done by changing the amplitude (AM), the frequency (FM) or the phase, or any combination of these
MoU
Memorandum of Understanding-
see GSM MoU
MPEG
Motion Picture Experts Group; MPEG4 is a technology for compressing voice and video so that the information can be transmitted over normally difficult links such as mobile radio
MS
Mobile Station
MSC
Mobile Switching Centre; the switching centre of a mobile phone network, the MSC has interfaces to the BSCs, HLR, VLR and other MSCs
MSISDN
Mobile Station International ISDN Number
MSK
Minimum Shift Keying; Another term for FFSK
Multiplexing
A telecommunications technique where several channels can be combined to share the same transmission medium. The most common forms are Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) and Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
MVPN
Mobile Virtual Private Network
N-AMPS
Narrowband AMPS
NB
Normal Burst; used to carry traffic and control channels except RACH
NET
Norme Europeenne de Telecommunications
NMT
Nordic Mobile Telephone system; an analogue cellular technology deployed in the Nordic countries in the late 1970 variations were also deployed in the Benelux countries and in Russia. NMT operated in the 450 and 900MHz bands and was the first technology to offer international roaming, albeit only in the Nordic countries
Node B
The element in a UMTS network which interfaces with the mobile station, analogous to a BTS in a GSM network
OTA
Over the air activation (of services and tariff changes)
O&M
Operations and Maintenance
OMC
Operations and Maintenance Centre
OMC-R
The radio OMC
OMC-S
The switching OMC
OSI
Open Systems Interconnection; a seven layer model for protocols defined by ISO
PACS
Personal Access Communication System; a digital cordless technology developed initially by Bell Labs in the US, PACS was designed to compete with DECT
Packet switching
A communication system wherein the information is transmitted in packets of a set size. These packets have address headers and find their way to their destination by the most efficient route through the network. Compared to circuit switching where a connection is occupied until the traffic exchange is completed, packet switching offers considerable efficiencies as connections can be used by a number of users simultaneously
PAMR
Public Access Mobile Radio; Commercial service using trunking techniques in which multiple groups of users can set up their own closed systems within a shared public network
PAP
Public Access Profile; a DECT term
PCH
Paging Channel; downlink only, the MS is informed of incoming calls by the BTS via the PCH
PCM
Pulse Code Modulation; the standard digital voice format at 64kbit/s
PCMCIA
Personal Computer Memory Card Interface Association the body responsible for defining the standards and formats for memory expansion cards for laptop computers and PDAs. Now extended to cover cards for mobile phones
PCN
Personal Communications Network; a designation initially used in the UK to refer to networks operating in the 1800MHz band (see also DCS1800). No longer in use
PCS 1900
Personal Communications Systems 1900MHz; the terminology used in the US to describe the new digital networks being deployed in the 1900MHz band; rarely used today
PCU
Packet Control Unit; an element in a GPRS/UMTS network
PDA
Personal Digital Assistant
PDC
Personal Digital Communications; a digital cellular technology developed and deployed uniquely in Japan. A TDMA technology, PDC is incompatible with any other digital cellular standard
PEDC
Pan European Digital Communications; A designation occasionally used in the early 1990â₠¬Ã¢â€žÂ¢s to describe GSM. No longer in use
Penetration
The percentage of the total population which owns a mobile phone
PHS / PHP
Personal HandyPhone System/Phone; a digital cordless technology developed in Japan which achieved great success. Deployed by NTT DoCoMo and other Japanese operators PHS offered two-way communications, data services and Internet access and eventually won some 28 million customers. Now in decline as cellularââ‚à ƒâ€šÃ‚¬ÃƒÂ¢Ã¢â‚¬Å¾Ã‚¢s wide area capabilities offer better service
PIN
Personal Identifier Number
PKI
Public Key Infrastructure
PLMN
Public Land Mobile Network; any cellular operator network
PMR
Private Mobile Radiocommunications; two-way radio technology widely used for despatch and delivery services, taxi companies and the like. See TETRA
POCSAG
Post Office Code Standardisation Group; a now defunct industry grouping which standardised pager addressing systems
PoP
Points of Presence; a method of measuring the value of a cellular licence; the approximate number of potential customers within a geographical area
POTS
Plain Old Telephone Service
PROM
Programmable Read Only Memory
PSK
Phase Shift Keying
PSRCP
Public Safety Radio Communications Project; an initiative by the UK Government to standardise all emergency services communications on to a single digital technology (see TETRA)
PSDN
Public Switched Data Network
PSPDN
Public Switched Packet Data Network
PSTN
Public Switched Telephone Network
PSU
Power Supply Unit
PTO
Public Telecommunication Operator
PTT
Posts, Telephone and Telegraph Administration
PTT
Push-to-Talk; a feature of PMR systems
PWT
Personal Wireless Telecommunications; a variant of DECT developed for use in the USA
QAM
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
QAPSK
Quadrature Amplitude Phase Shift Keying
QCELP
Quadrature Code Excited Linear Prediction
QoS
Quality of Service; a broad term to describe the performance attributes of an end-to-end connection
QPSK
Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
RACE
Research in Advanced Communications in Europe
RACH
Random Access Channel; uplink only, allows the MS to request an SDCCH in response to a page or for a call
RAM
Random Access Memory
RFP
Radio Fixed Part; equivalent to a base station in a DECT system
RCC
Radio Common Carrier
RELP
Regular pulse Excitation Linear Prediction coding
Reuse
The assignment of frequencies or channels to cells so that adjoining cells do not use the same frequencies and cause interference whereas more distant cells can use the same frequencies. Reuse expands the capacity of a cellular network by enabling the use of the same channels throughout the network
RP
Radio Part
RNC
Radio Network Controller; the element which controls the Node Bs within a UMTS network. It is roughly analogous to a BSC in a GSM network
Roaming
A service unique to GSM which enables a subscriber to make and receive calls when outside the service area of his home network e.g. when travelling abroad
Router
A device which forwards information in a network on a connectionless basis
RRM
Radio Resource Management, part of the UMTS infrastructure
RT
Remote Terminal
SACCH
Slow Associated Control Channel; transmits continuous measurements in parallel with operation of TCH or SDCCH; needed for handover decisions
SAR
Specific Absorption Rate
SB
Synchronisation Burst; used for time synchronisation of the mobile
S-CDMA
Synchronous CDMA (see CDMA)
SCH
Synchronisation Channel; downlink only frame synchronisation and identification of base station
SCP
Switching/Service Control Point
SDCCH
Stand-alone Dedicated Control Channel; communications channel between the MS and the BTS. Used for signalling during call set-up before a TCH is allocated
SDLC
Synchronous Data Link Control
SDMA
Spatial Division Multiple Access
SGSN
Serving GPRS Support Node; the gateway between the RNC and the core network in a GPRS/UMTS network
SIM
Subscriber Identity Module; A smart card containing the telephone number of the subscriber, encoded network identification details, the PIN and other user data such as the phone book. SIM card can be moved from phone to phone as it contains all the key information required to activate the phone
SoHo
Small Office/Home Office
Streaming
An Internet derived expression for the one-way transmission of video and audio content
STK
SIM ToolKit: specified within the GSM standard, this allows operators to add additional functions to the phone menu in order to provide new services such as mobile banking or email
SMR
Specialised Mobile Radio; the US term for private mobile radio (See PMR)
SMS
Short Message Service; a text message service which enables users to send short messages (160 characters) to other users. A very popular service, particularly amongst young people, with 400 billion SMS messages sent worldwide in 2002
SMSC
SMS Centre-the network entity which switches SMS traffic
SMSCB
SMS Cell Broadcast
SMS-MO
SMS Mobile Originated
SMS-MT
SMS Mobile Terminated
SMS-PP
SMS Point to Point
SP
Service Provider
SQAM
Staggered Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
SQPSK
Staggered Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
SS
Supplementary Service Support; handles special services
SS7
Signalling System Number 7 (See CCS7)
SSP
Service Switching Point
STM
Synchronous Transfer Mode
Symbian
A company created by Psion, Nokia, Ericsson and Motorola in 1998 with the aim of developing and standardising an operating system which enable mobile phones from different manufacturers to exchange information
The operating system is known as EPOC. Matsushita has subsequently joined Symbian
TACS
Total Access Communications System (an AMPS variant deployed in a number of countries principally the UK)
TAP
Transferred Account Procedure; the essential charging methodology for international GSM roaming. There have been four TAP standards, TAP1, TAP2, TAP2+ and TAP3. The latter offers variable record length and is sufficiently flexible to support all future requirements arising from the move to 3G
TBR
Technical Basis for Regulation (part of the ETSI standardisation process)
TCH
Traffic Channel
TD-CDMA
Time Division CDMA
TD-SCDMA
Time Division-Synchronous CDMA; a CDMA variant developed by Chinese vendors which is claimed to offer high data rates and greater coverage
TDD
Time Division Duplex; a radio technology for use in unpaired spectrum. WCDMA/UMTS includes a band for TDD mode usage and both PHS and DECT use this technology
TDMA
Time Division Multiple Access; a technique for multiplexing multiple users onto a single channel on a single carrier by splitting the carrier into time slots and allocating these on a as-needed basis
Telematics
A wireless communications system designed for the collection and dissemination of information, particularly refers to vehicle-based electronic systems, vehicle tracking and positioning, on-line vehicle navigation and information systems and emergency assistance
TETRA
Terrestrial Trunked Radio; a European developed digital private mobile radio technology which is now being extensively deployed worldwide
Tetrapol
A competitive digital PMR technology to TETRA developed by French vendors
TFTS
Terrestrial Flight Telephone System
Timeslot
A frame within a TDMA schema; has a time interval of 576 microseconds. Physical content of a timeslot is known as a burst. Five different burst types exist, they are distinguished by different TDMA frame divisions (see NB, FB, SB, AB and DB)
TIPHON
Telecommunications and Internet Protocol Harmonisation over Networks; an ETSI project designed to support the market for voice communications and voice band communications. In particular TIPHON will ensure that users on IP-based networks can communicate with those on circuit switched networks
TMN
Telecommunications Management Network
TMSI
Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity; covers the IMSI to prevent over-the-air interception and tracing
TRAU
Transcoder Rate Adapter Unit; the transport unit for a 16kbit/s traffic channel on the A-bis interface
Tri-band
Refers to a mobile phone able to operate on the three internationally designated GSM frequencies- 900, 1800 and 1900MHz
TrueSync
A technology which enables the optimal synchronisation of calendars, address books, action lists and memoranda. It enables multi-point, one-step synchronisation of wireless and wireline devices, desktop computers and server-based applications and services
TRX
Transmitter/receiver (transceiver)
Total Access Communications System (an AMPS variant deployed in a number of countries principally the UK)
UI
User Interface
Um
The air interface between the BTS and the MS in a GSM network
Uu
The air interface between the Node B and the MS in a UMTS network. thanks for sharing... | |
|   | | sansam
AMCT MEMBER



Age : 36
Job/hobbies : admin
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Mon Jun 27, 2011 1:51 pm Mon Jun 27, 2011 1:51 pm | |
| Thanks for the useful info's'... | |
|   | | strongest24
STUDENTS SUPPORTER



Age : 42
Job/hobbies : technician
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Sat Aug 13, 2011 8:48 am Sat Aug 13, 2011 8:48 am | |
| | |
|   | | dayjoss
NEW MEMBER



Age : 51
Job/hobbies : musica
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Mon Feb 27, 2012 3:34 am Mon Feb 27, 2012 3:34 am | |
|  tank friend the material is very good | |
|   | | kimx44
FORUM SUPPORTER



Age : 51
Job/hobbies : technician
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Mon Jun 04, 2012 7:24 am Mon Jun 04, 2012 7:24 am | |
| | |
|   | | kimx44
FORUM SUPPORTER



Age : 51
Job/hobbies : technician
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  Thu Sep 20, 2012 2:40 am Thu Sep 20, 2012 2:40 am | |
| | |
|   | | Sponsored content
 |  Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks Subject: Re: Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks  | |
| |
|   | | | | Sticky: Collection Mobile Tips & Tricks |  |
|
Similar topics |  |
|
| | Permissions in this forum: | You cannot reply to topics in this forum
| |
| |
| |
|





